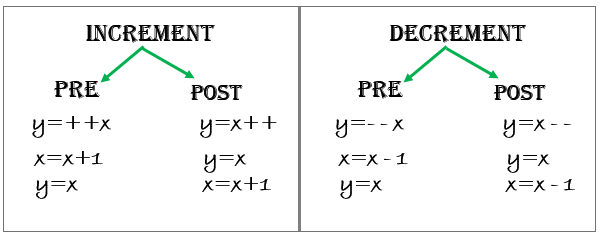
Increment and Decrement Operators
Əgər operator dəyişəndən (operand) əvvəl gəlirsə, pre-increment (++a) və pre-decrement (--a) operator adlanır. Bu zaman operator əvvəlcə tətbiq/icra edilir və dəyişənin yeni dəyəri geri qaytarılır. Müvafiq olaraq, əgər operator dəyişəndən (operand) sonra gəlirsə, post-increment (a++) və post-decrement (a--) operator adlanır. Bu zaman isə əvvəlcə dəyişənin orijinal dəyəri geri qaytarılır və operator dəyər qaytarıldıqdan sonra icra edilir.
int x = 3;
int y = ++x * 5 / x-- + --x;
System.out.println("x is " + x); // x is 2
System.out.println("y is " + y); // y is 7
Addım-addım baxaq:
int y = 4 * 5 / x-- + --x; // x assigned value of 4 int y = 4 * 5 / 4 + --x; // x assigned value of 3 int y = 4 * 5 / 4 + 2; // x assigned value of 2
Bu sualın izahı əksər oxucular tərəfindən qarışdırılır, hətta Coderanch forumunda da bu nümunənin izahı ilə bağlı 10-dan çox post var. Onlardan 2 ən maraqlısının linkini aşağıda qeyd etmişəm:
- https://coderanch.com/t/649218/certification/wiley-oca-book-error-unary
- https://coderanch.com/t/669054/certification/Priority-Post-Pre-Unary-Operators
char ilə bağlı bir nümunəyə baxaq:
char c = 'c'; System.out.println(++c); // output: d System.out.println(++'c'); // DOES NOT COMPILE
Casting Primitive Values
Daha böyük tipdən (numerical) daha kiçik tipə və yaxud onluq saydan tam ədədə keçmək üçün casting istifadə olunur.
int x = (int)1.0; short y = (short)1921222; // Stored as 20678 int z = (int)9f; long t = 192301398193810323L;
Overflow:
int i = 2147483647+1; // -2147483648 int i2 = 2147483648; // DOES NOT COMPILE byte b = (byte) (128+128); // 0 System.out.println(i+b); //-2147483648
Bir sıra digər maraqlı nümunələrə baxaq:
short x = 10; short y = 3; short z1 = x * y; // does NOT compile short z2 = (short) x * y; // does NOT compile short z3 = (short)(x * y); // does compile byte b1 = (byte)1000 + (byte)1000; // output: -48 byte b2 = (byte)100 + (byte)100; // DOES NOT COMPILE byte b3 = (byte)100 + (byte)27; // output: 127
[topics lang=az]